Comparative Effectiveness of Antibiotics for Empirical Treatment initiated for Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Pediatric and Adult Populations
Funding Agency: Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) in collaboration with Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute (MGMCRI).
Objective
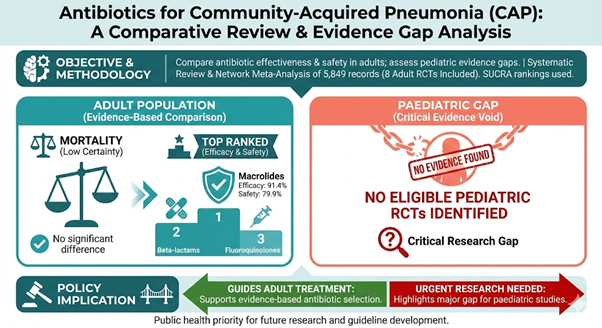
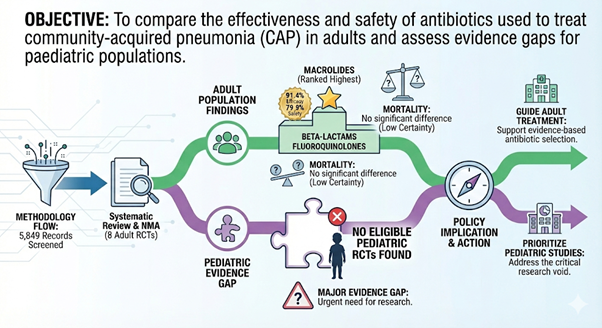
The primary objective was to systematically compare the effectiveness and safety profiles of different antibiotic classes used for the empirical, initial treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) in both children and adults.
Methodology
A comprehensive evidence synthesis approach was utilized to evaluate clinical outcomes, symptom resolution, and complication rates across multiple antibiotic regimens. The study analyzed high-quality comparative data to identify optimal treatment choices for varying severities of CAP.
Key Findings
Amoxicillin emerged as the most effective and safest first-line antibiotic for treating non-severe CAP in children. For adults with non-severe CAP, amoxicillin and amoxicillin/clavulanic acid demonstrated superior therapeutic success and faster recovery. In cases of severe CAP, fluoroquinolones particularly moxifloxacin were found to deliver significantly better clinical outcomes. These findings provide strong evidence to inform and update national clinical guidelines.