Exploring Sex and Gender Sensitivity in Diabetes Care Guidelines: A Guideline Review
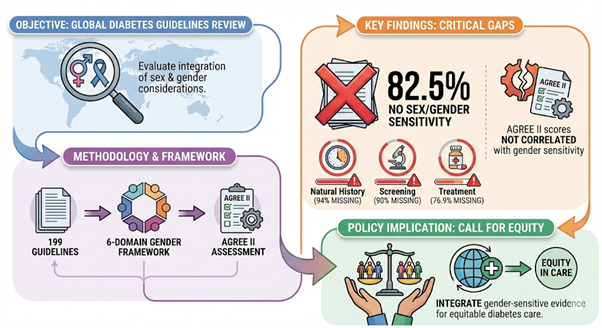
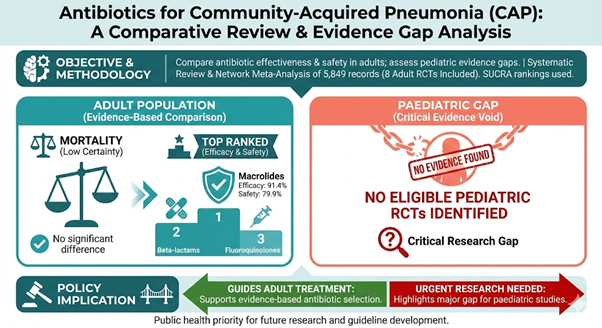
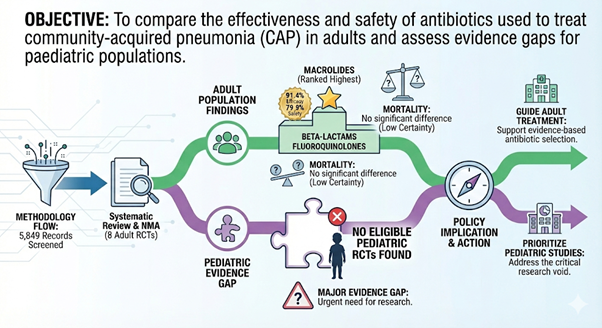
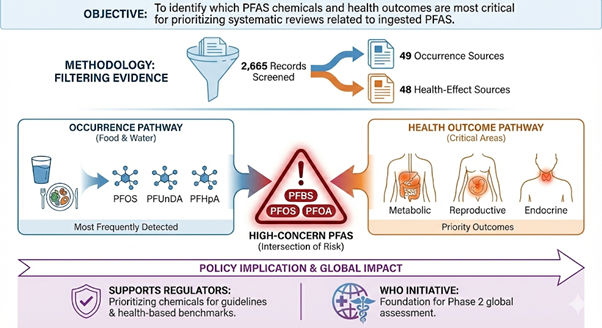
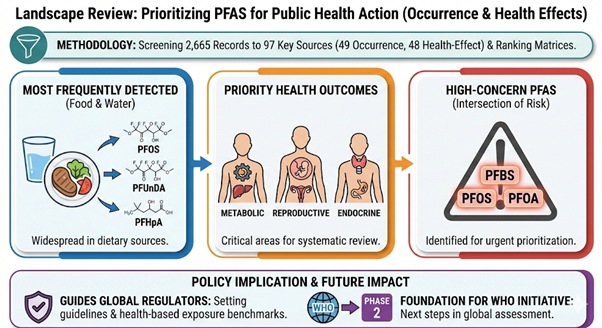
Funded by: DIWAS Objective The project aimed to systematically assess the extent to which national and international diabetes mellitus clinical practice guidelines incorporate sex-specific (biological) and gender-related (socio-cultural) variations in diabetes risk, diagnosis, clinical management, and outcomes. Methodology A structured guideline review framework was applied to evaluate sex and gender [...]