Applying a Gender Lens to Diabetes Care: A Monograph
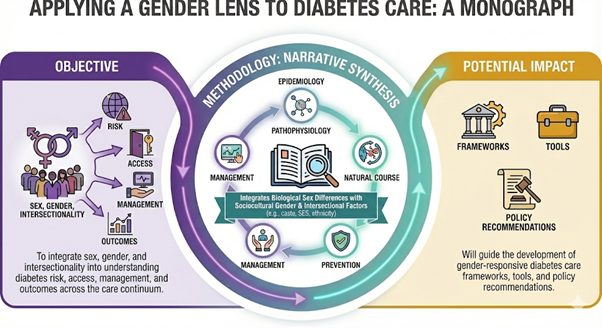
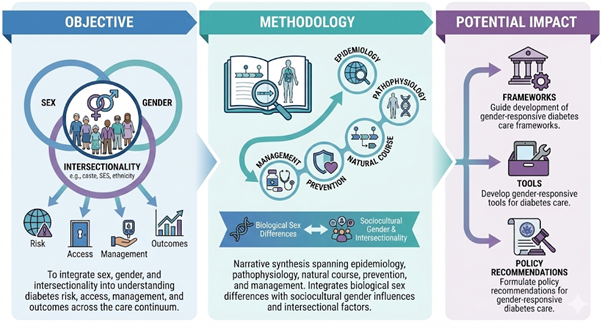
Funded by: DIWAS Objective The objective is to translate evidence into actionable, women-centred frameworks that help clinicians and policymakers integrate gender considerations into diabetes management. It aims to improve real-world practice through clear, structured, and context-sensitive recommendations. Methodology The project compiles chapter-based guidance, case narratives, checklists, and training modules into [...]